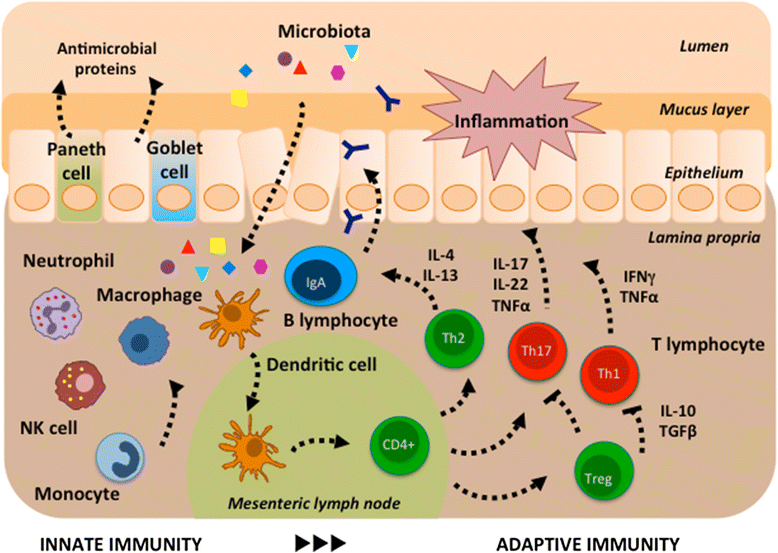
Macrophages secrete cytokines which then activates neutrophils and dilates the blood stream so that more proteins can arrive at the scene. If it's an infection, the message also gets to T-cells (in vertebrates) which will then activate B-Cells, and then pretty much destroy anything.
Full Answer
What is the function of macrophages?
Apr 13, 2018 · Macrophages secrete cytokines which then activates neutrophils and dilates the blood stream so that more proteins can arrive at the scene. If it's an infection, the message also gets to T-cells (in vertebrates) which will then activate B …
What are macrophages Quizlet?
Question: 2. Macrophages secrete which then activates O interleukin-1: cytotoxic T cells interleukin-2: cytotoxic T cells interleukin-2; helper T cells interleukin-1: helper T cells 3. Cytotoxic T cells target and destroy individual isolated antigens infected "self" cells OB cells macrophages 4. Helper T cells stimulate the proliferation of ...
How are macrophages activated?
Oct 07, 2014 · Following this recognition, T lymphocytes release cytokines that activate B cells, and activated B lymphocytes then secrete antibodies specific to the antigens presented by the macrophage. These antibodies attach to antigens on microbes, or to cells invaded by microbes; in turn, these antibody-bound complexes are phagocytosed more avidly by ...
What produces antibodies Quizlet?
Activation of macrophages to kill tumor cells is a slow process (generally 1-3 days) M2 – “fixes,” wound healing; secretes arginase; favor development of new blood vessels in oxygen-starved tissues (called angiogenesis or neovascularization), such as at the back of the eyes (macular degeneration; diabetic retinopathy); promotes spread of tumors (metastasis).

What does macrophage release?
When macrophages are exposed to inflammatory stimuli, they secrete cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF), IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-12. Although monocytes and macrophages are the main sources of these cytokines, they are also produced by activated lymphocytes, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts.Oct 7, 2014
What is the role of macrophage in immune response?
Macrophages work as innate immune cells through phagocytosis and sterilization of foreign substances such as bacteria, and play a central role in defending the host from infection.Dec 29, 2017
Do macrophages release antibodies?
Eventually, the antigen presentation results in the production of antibodies that attach to the antigens of pathogens, making them easier for macrophages to adhere to with their cell membrane and phagocytose. In some cases, pathogens are very resistant to adhesion by the macrophages.
When is adaptive immunity activated?
Adaptive immunity is an immunity that occurs after exposure to an antigen either from a pathogen or a vaccination. This part of the immune system is activated when the innate immune response is insufficient to control an infection.
How are macrophages activated?
Macrophages are activated by interferon-γ (IFN-γ) from various sources – including activated NK cells or T cells – or by non-immunologic stimuli such as endotoxin.
What cells do macrophages activate?
Macrophages interact with T cells in order to bring about T cell activation in target organs, and are themselves activated by inflammatory messenger molecules (cytokines) produced by the T cells. Macrophages produce toxic chemicals, such as nitric oxide, that can kill surrounding cells.
When are macrophages activated?
Macrophage activation takes place in two separate steps during transplantation: initially, macrophages become activated as a result of the tissue injury associated with ischemia-reperfusion, leading to early graft damage. Then they become activated in response to danger signals produced by the miss-matched transplant.
Do macrophages secrete histamine?
Macrophages (M phi) produce histamine (Hm) when activated by bacterial endotoxin (LPS) through induced histidine decarboxylase (HDC).
How are macrophages produced?
Macrophages are formed through the differentiation of monocytes, one of the major groups of white blood cells of the immune system. When there is tissue damage or infection, the monocytes leave the bloodstream and enter the affected tissue or organ and undergo a series of changes to become macrophages.Nov 11, 2019
What activates the adaptive immune system?
To achieve functional adaptive immune responses, antigen-specific T cell populations are stimulated by professional antigen-presenting cells like dendritic cells (DCs), which provide crucial stimulatory signals for efficient expansion and development of effector functions.
What is innate and adaptive immunity?
The main purpose of the innate immune response is to immediately prevent the spread and movement of foreign pathogens throughout the body. The second line of defense against non-self pathogens is called adaptive immune response.
Are antibodies innate or adaptive?
Innate and adaptive immunity time line. The mechanisms of innate immunity provide the initial defense against infections....Innate and Adaptive Immunity.InnateAdaptiveBlood proteinsComplement, othersAntibodiesCellsPhagocytes (macrophages, neutrophils), natural killer cells, innate lymphoid cellsLymphocytes7 more rows
Popular Posts:
- 1. how to legit activate win 10 through microsoft
- 2. how to activate the show danger zone
- 3. how to activate 3/3 offer telenor talkshawk
- 4. how to activate cable modem on xfinity
- 5. how to activate chrome
- 6. how to activate a stolen verizon phone
- 7. how to activate a tmobile phone
- 8. how do i activate the keyboard on my tablet?
- 9. how to activate primium key printershare
- 10. why is my ps4 telling me to activate as primary